IUPAC Name - 2-carbamoyloxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium;chloride
Synthesis
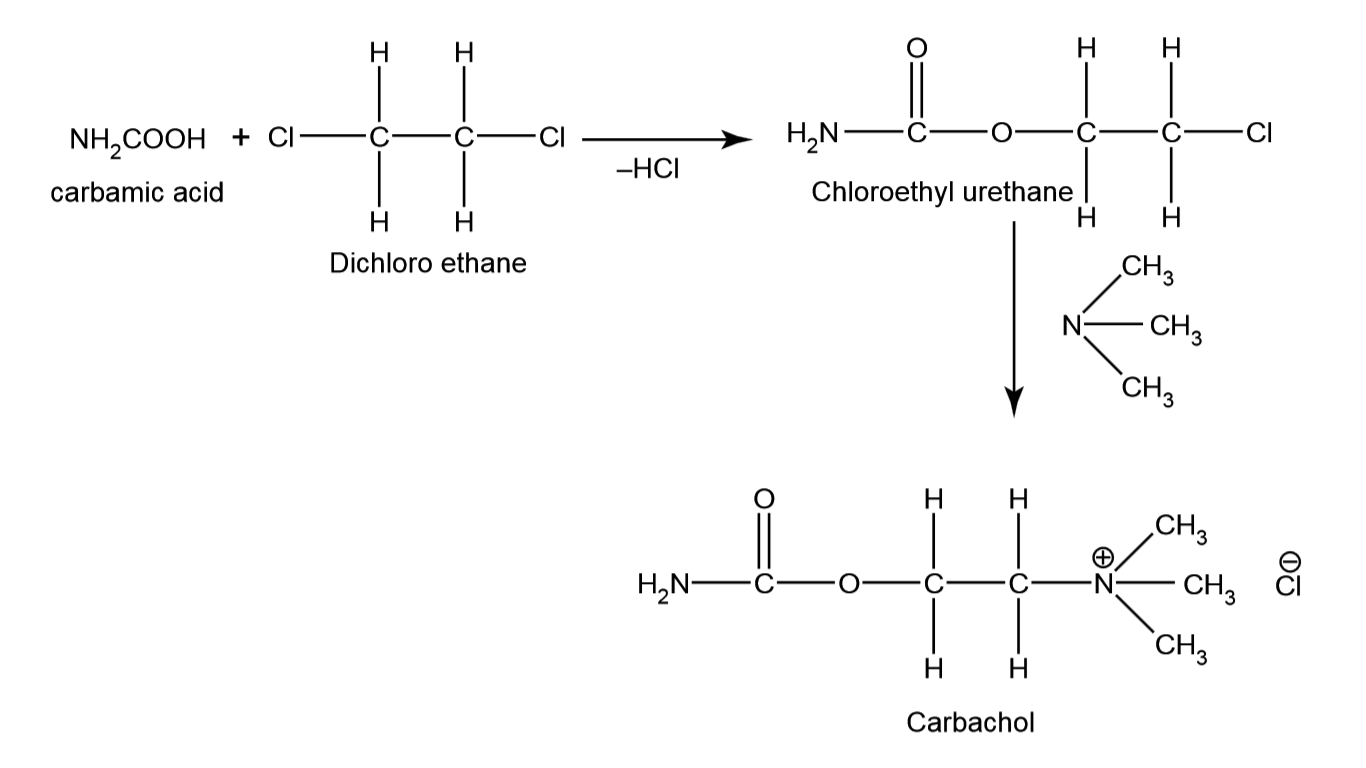
From Carbamic Acid
Step 1 : Carbamic acid is reacted with
dichloro ethane. Simple condensation
reaction takes place,
HCl is removed, Chloroethyl urethane is
formed.
Step 2 : To chloroethyl urethane,
Trimethyl amine is added (Ammonia, in
which all hydrogen is replaced with methyl), carbachol results.
Mechanism of Action
It possess both muscarinic and nicotinic properties by
cholinergic receptor stimulation.
Uses
It is used for its
miotic actions in the
treatment of glaucoma to reduce intraocular pressure.
Adverse effects
No frequent / severe adverse effects

