Classification
Short acting:
Sulfadiazine
Intermediate acting:
Sulfamethoxazole
Long acting: Sulfadoxine,
Sulfamethopyrazine
Special purpose: Sulfscetamide
Sodium, Sulfasalazine, Silver sulfadiazine, Mafenide
Uses
Meningitis
Streptococcal pharyngitis
Sulphamethoxazole + Trimethoprim
(Cotrimoxazole) is used for many bacterial infections &
P.jiroveci.
Conjunctivitis -
Sulfacetamide Sodium
Prevent infection on burn surfaces -
Silver Sulfadiazine (topical)
Mechanism of Action
Sulphonamides are
structural analogues of PABA. Thus inhibit bacterial folate synthase, Folic
acid is not formed and a number of essential metabolic reactions suffer.
Note: Only those microbes which synthesize their own folic acid and
cannot take it from the medium are susceptible to sulfonamides.
Adverse Effects
Nausea, Vomiting and
epigastric pain.
Crystalluria (dose related) - Occurs due to acetylated
derivatives of sulphonamidea are not soluble in urine.
Hypersensitivity reactions
Kernicterus (new born)
Structure - Activity Relationship
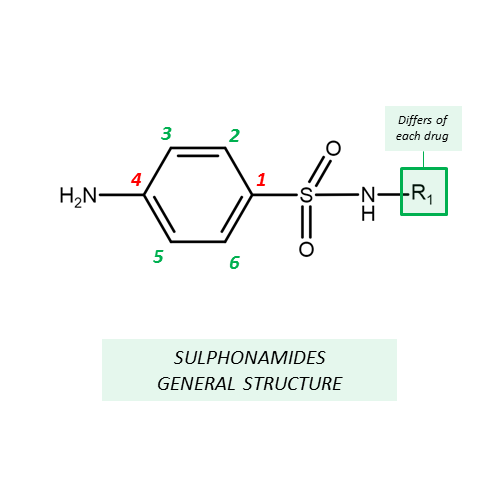
General Structure
- Sulfonamides are derivatives of sulfanilamide -
para-amino benzene sulfonamide.
- Differs in the N1 substitution of
sulfanilamide.
SAR
• Amino (-NH2) group should be in 4th position and Sulphonyl (-SO2) group
should be in the 1st position. Essential for activity.
• N-4 amino group could be modified to be pro-drugs.
• Replacement of benzene ring
by other ring system decreases or abolishes activity.
• Substitutions on benzene ring
decreases activity.
• Substituents imparting electron-rich characters to SO2 group, on N-1,
increases bacteriostatic activity.


0 Comments