Carbachol is a directly acting parasympathetic agent.
Carbachol is rarely used clinically.
Synonym: Carcholin, Moistat
IUPAC Name:
Synthesis:
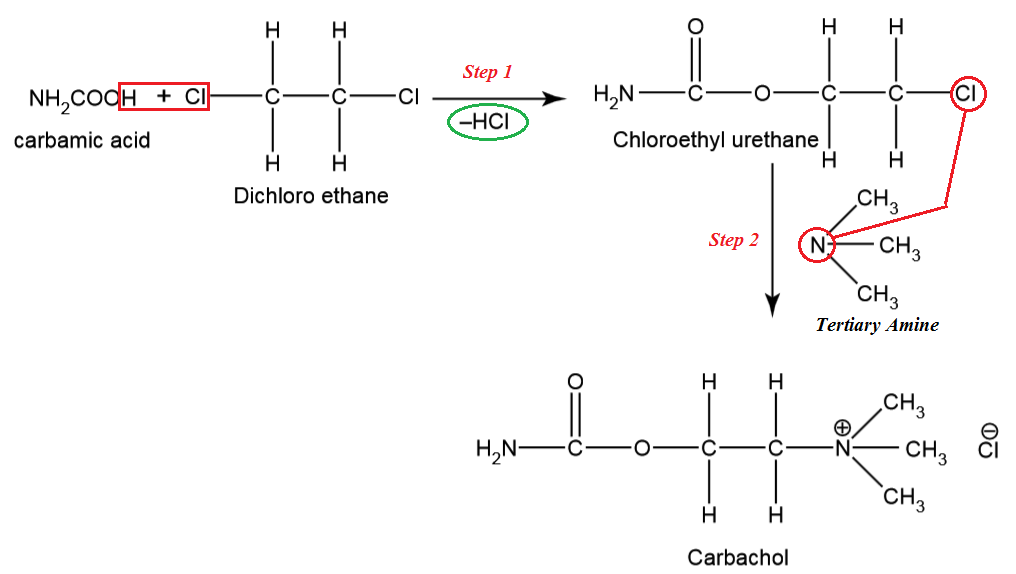
Step 1: We are using carbamic acid and dichloroethane
as starting materials to synthesize carbachol. On adding dichloroethane to
carbamic acid, HCL is removed (H from carbamic acid and –Cl from dichloroethane) and chloroethyl urethane is produced.
Step 2: To Chloroethyl urethane, the tertiary amine is
added. Carbachol is produced.
Adverse Effects: At therapeutic dose (ophthalmologically), little or no side effects occur due to lack of systemic penetration.
- People may experience vision problems - seeing floaters
- Eye irritation or burning like sensation
Mechanism of Action:
Carbachol acts similar to acetylcholine.



0 Comments