Neostigmine bromide is an indirectly acting parasympathomimetic agent. The action is produced by blocking the cholinesterase enzyme which breakdown the acetylcholine. Hence, there is an increase in the availability of acetylcholine.
IUPAC
3-{[(Dimethylamino)carbonyl]oxy}-N,N,N-trimethyl benzene ammonium bromide
Synonyms of neostigmine
Prostigmine, Myostigmin, Tilstigmin
Route of synthesis
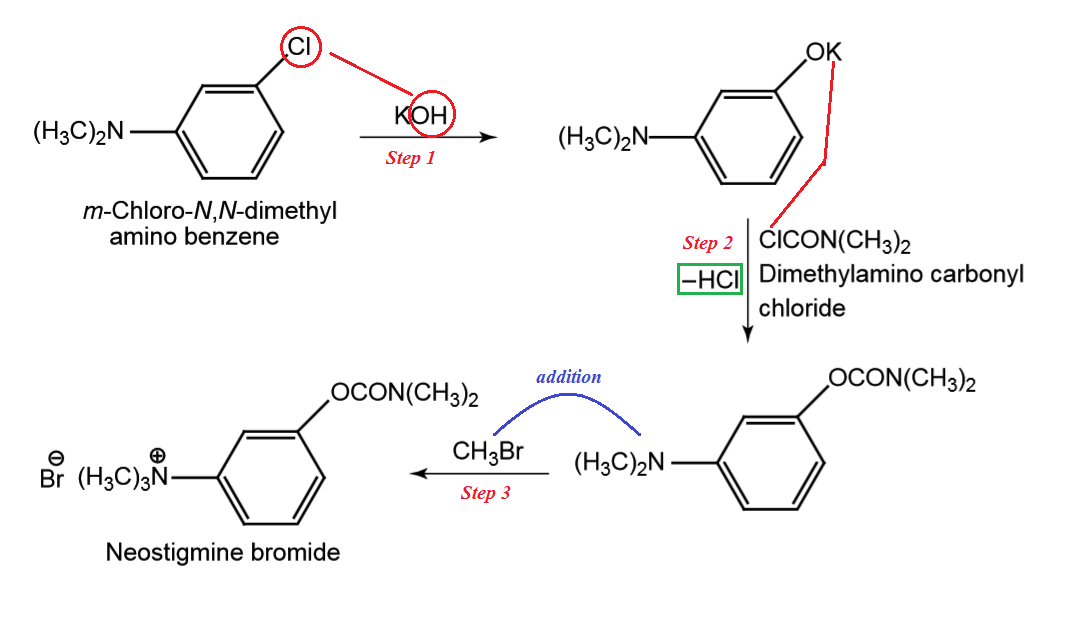
Separate neostigmine into three parts - Benzene Ring, Trimethyl Ammonium group, and Dimethylaminocarbonyl group. Keeping in mind, we selected "m-chloro-N,N-dimethyl amino benzene" as starting material. To this, adding potassium hydroxide (KOH) results in an intermediate compound.
To the intermediate compound, add dimethylamino carbonyl chloride. Again, K + Cl is removed and intermediate is produced.
Now, in the last step, add methyl bromide (CH3Br). Simple, addition takes place in the dimethylamino group and it becomes neostigmine bromide.
Mechanism of Neostigmine
Enzyme inhibition
Neostigmine and other indirectly acting parasympathomimetics inhibit enzyme acetylcholinesterase reversibly. This results in greater availability of acetylcholine at its site of action.



0 Comments